You are here: Start » Function Reference » Image » Image Local Transforms » GradientDirAndPresenceImage
GradientDirAndPresenceImage
| Header: | FIL.h |
|---|---|
| Namespace: | fil |
| Module: | FoundationBasic |
Computes an image of gradient directions mapped to the range from 1 to 255. Zero means "no edge".
Applications: For highly optimized analysis of gradient directions.
Syntax
void fil::GradientDirAndPresenceImage ( const fil::Image& inImage, ftl::Optional<const fil::Region&> inRoi, fil::GradientMaskOperator::Type inOperator, float inEdgeThreshold, fil::AngleRange::Type inAngleRange, fil::Image& outDirectionsImage )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Range | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inImage | const Image& | Input image | ||
 |
inRoi | Optional<const Region&> | NIL | Range of output pixels to be computed | |
 |
inOperator | GradientMaskOperator::Type | Defines how the gradient is computed | ||
 |
inEdgeThreshold | float | 0.01 - 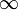 |
10.0f | Minimum edge magnitude (other pixels will be set to 0) |
 |
inAngleRange | AngleRange::Type | _0_360 | Range of output angles | |
 |
outDirectionsImage | Image& |
Description
The operation computes the angle of the intensity change direction at each pixel of the inImage. Firstly the selected inOperator is used to obtain two-dimensional gradient vector at each pixel. When this vector length exceeds inEdgeThreshold the angle of the vector is calculated, scaled and stored in outDirectionsImage pixel.
This operation always generates a single-channel image with the uint8 pixel type on the output, regardless of the input image format, with following pixel values:
- When gradient length does not exceed threshold, the value of 0 is stored in pixel.
- When gradient length exceeds threshold, its angle is scaled to range 0..255 and stored in pixel value.
When a pixel value is non-zero, one can restore the original angle with the formula:
double angle = value * 360.0 / 255.0; // if inAngleRange == _0_360 double angle = value * 180.0 / 255.0; // if inAngleRange == _0_180 double angle = value * 90.0 / 255.0; // if inAngleRange == _0_90
To measure the angular distance between two directions described by two non-zero pixel values, use the following formulas:
int valueDif = abs(inValue1 - inValue2); double angleDif = (valueDif < 128 ? (double)valueDif : (255.0 - valueDif)) * 360.0 / 255.0; // if inAngleRange == _0_360 double angleDif = ((double)valueDif) * 180.0 / 255.0; // if inAngleRange == _0_180 double angleDif = ((double)valueDif) * 90.0 / 255.0; // if inAngleRange == _0_90
Hardware Acceleration
This operation is optimized for SSE41 technology for pixels of type: UINT8.
This operation is optimized for AVX2 technology for pixels of type: UINT8.
This operation is optimized for NEON technology for pixels of type: UINT8.
This operation supports automatic parallelization for multicore and multiprocessor systems.
Errors
List of possible exceptions:
| Error type | Description |
|---|---|
| DomainError | Region exceeds an input image in GradientDirAndPresenceImage. |
See Also
- GradientImage_Mask – Computes a gradient image with a Sobel or Prewitt operator.
- GradientImage – Computes a gradient image with smoothing operator of any size. The output pixels are signed.
- GradientMagnitudeImage – Measures the strength of gradient at each pixel location.

