You are here: Start » Program Examples » Plate Measurement (Advanced)
Plate Measurement (Advanced)
Aim:
The aim of the program is to measure the length of a metal plate.
Input:
An image of a metal plate.

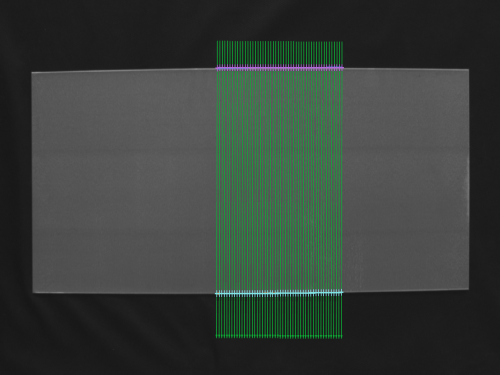
Output:
The image of the metal plate with marked segments connecting the edges vertically and information about the plate's length.
Hints:
This is the advanced variant of the Plate Measurement example. Here we use an analogous approach. However, some advanced tools are applied, so if you do not feel secure enough, we recommend taking a look at the Plate Measurement example first.
Labeling connections is explained in this article.
Solution (FIS):
-
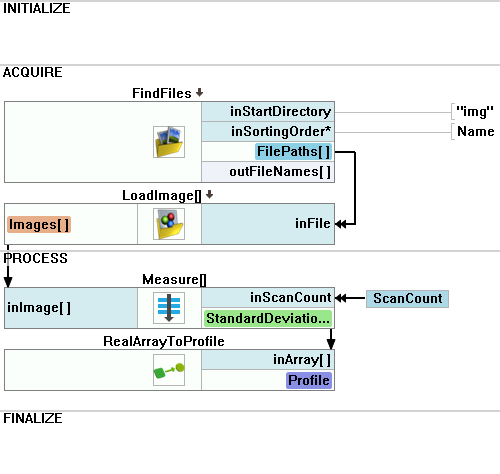
Add the FindFiles filter to enumerate images in an array mode.
-
Add the LoadImage filter and connect the outFilePaths to the inFile.
-
Add a new step macrofilter Measure. Connect the outImage to its inputs.
-
In Project Explorer find the Create New Global Parameter button, click it, and:
- Set name to ScanCount,
- Set type to IntegerArray,
- Set values: 5, 10, 20, 30, 50. This will allow you to perform several width measurements with a different number of scans each time. When widths in each iteration are eventually computed, output data is collected in an array, and in this way, some statistics (like standard deviation) can be calculated.
-
Connect ScanCount to the macrofilters inputs as an array connection and step inside it.
-
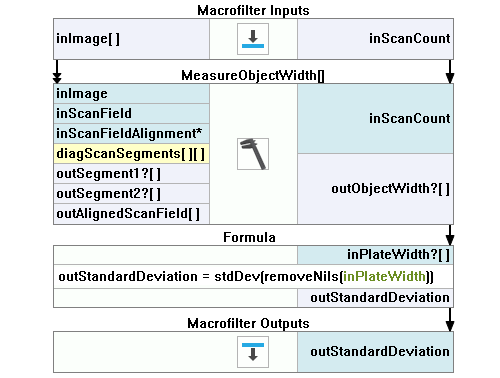
Add the MeasureObjectWidth filter to compute the width, which is the most suitable filter to use in this case.
-
Connect the macrofilter's inInput to the inImage.
-
Connect the macrofilter's inScanCount to the inScanCount.
-
Click on the MeasureObjectWidth filter and make these changes in the Properties window (in the left bottom corner):
- Define a scanning field in the inScanField vertically, and let it be wide enough (for example, one third of the plate's width).
- Set the inStripeScanParams.StripePolarity to Bright, because the plate is slightly brighter than the background, and it may not be detected properly otherwise.
- Set the inStripeScanParams.MinStripeWidth to 500 to make sure that some false edges are not detected.
-
Add the Empty formula filter and create an input using the outObjectWidth output.
-
Create a new output outStandardDeviation of Real type, remove Nil values from it and compute standard deviation, using the following command:
- outStandardDeviation = stdDev(removeNils(inPlateWidth))
- outStandardDeviation = stdDev(removeNils(inPlateWidth))
-
Connect the outStandardDeviation to macrofilter outputs as outStandardDeviation.
-
Go back to the Main and add the RealArrayToProfile filter to get a profile from an array of Real values. Connect the outStandardDeviation from Measure macrofilter with the inArray. As you can see, based on the profile, that the more scans are performed, the more precise measurement is (standard deviation gets gradually lower).
Macrofilter Main
Macrofilter Measure
Used Filters
| Icon | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FindFiles | Returns files of the input directory. | |
| LoadImage | Loads a single image from a file. | |
| MeasureObjectWidth | Measures the width of an object using stripe detection. | |
| RealArrayToProfile | Converts an array of real numbers to a profile. |
Further Readings
- 1D Edge Detection - The article explaining how edge detection filters work.

