You are here: Start » Function Reference » Computer Vision » 2D Edge Detection » DetectEdges_AsRegion_Mask
DetectEdges_AsRegion_Mask
| Header: | FIL.h |
|---|---|
| Namespace: | fil |
| Module: | FoundationBasic |
Extracts a pixel-precise region of continuous edges. Faster, yet less accurate version.
Applications: Consistent detection of pixels that belong to contours of variable or unpredictable shape, e.g. screw thread outline or a custom piece of textile.
Syntax
void fil::DetectEdges_AsRegion_Mask ( const fil::Image& inImage, ftl::Optional<const fil::Region&> inRoi, fil::EdgeMaskFilter::Type inEdgeMaskFilter, float inEdgeThreshold, float inEdgeHysteresis, float inMaxJoiningDistance, const int inMinBlobArea, fil::Region& outEdgeRegion, fil::Image& diagGradientMagnitudeImage )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Range | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inImage | const Image& | Image from which edges will be extracted | ||
 |
inRoi | Optional<const Region&> | NIL | Region of the image from which edges will be extracted | |
 |
inEdgeMaskFilter | EdgeMaskFilter::Type | Type of edge filter used for computing gradients | ||
 |
inEdgeThreshold | float | 0.0 -  |
35.0f | Sufficient edge strength; edges of that strength will always be detected |
 |
inEdgeHysteresis | float | 0.0 -  |
15.0f | Value by which the edge threshold is decreased for edge points neighboring with sufficiently strong edges |
 |
inMaxJoiningDistance | float | 0.0 -  |
0.0f | Maximal distance between edges that can be joined |
 |
inMinBlobArea | const int | 0 -  |
1 | Minimal area of an edge blob |
 |
outEdgeRegion | Region& | Region of the found edges | ||
 |
diagGradientMagnitudeImage | Image& | Visualization of the gradient magnitude |
Description
The operation extracts edges from the inRoi region in the inImage image and stores the result in the outEdgeRegion region. The extraction process is the same as in DetectEdges_AsPaths_Mask, the only difference being the data type of the result. This filter returns a region rather than array of subpixel-precise paths computed by DetectEdges_AsPaths_Mask.
The extraction process starts from gradient computing, what is done using chosen non-recursive filter with fixed size mask.
On the so computed gradient image threshold with hysteresis (as in ThresholdImage_Hysteresis) is performed with inEdgeThreshold and inEdgeHysteresis parameters. After this step only gradients which are strong enough are present. The resulting edge region can be much too thick, thus it has to be thinned. To achieve this, the non-maximum suppression is used. Every pixel with at least one of its neighbors having larger gradient is no longer considered to be an edge pixel (only neighbors in the direction of pixel's gradient matter).
Examples
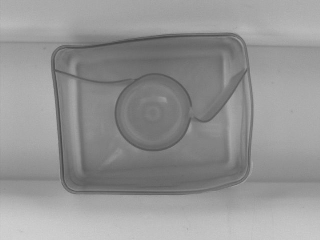 |
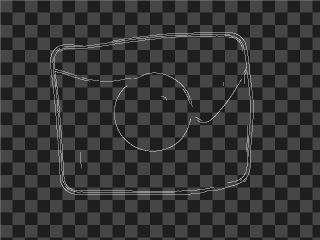 |
DetectEdges_AsRegion_Mask performed on the sample image with inEdgeMaskFilter = Sobel, inEdgeThreshold = 20, inEdgeHysteresis = 5.
Hardware Acceleration
This operation supports automatic parallelization for multicore and multiprocessor systems.
Errors
List of possible exceptions:
| Error type | Description |
|---|---|
| DomainError | Unsupported edge mask filter in DetectEdges_AsRegion_Mask. |
See Also
- DetectEdges_AsRegion – Extracts a pixel-precise region of continuous edges.
- DetectEdges_AsPaths – Extracts subpixel-precise paths that represent continuous edges.
- DetectEdges_AsPaths_Mask – Extracts subpixel-precise paths that represent continuous edges. Faster, yet less accurate version.

