You are here: Start » FIL.NET » Function Reference » Region » Region Global Transforms » FIL.SplitRegionIntoComponents
Splits a region into an array of regions. Operates by merging blobs in accordance to the inMaxDistance parameter.
| Namespace: | FilNet |
|---|---|
| Assembly: | FIL.NET.dll |
Syntax
C++
C#
public static void SplitRegionIntoComponents ( FilNet.Region inRegion, float inDistanceBalance, int inMinComponentArea, bool inRemoveBoundaryBlobs, IList<FilNet.Region> outComponents )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Range | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | inRegion | FilNet.Region | Input region. | ||
 | inDistanceBalance | float | <-1.0f, 1.0f> | Defines how much important the distance between regions in x coordinate is according to distance in y coordinate. | |
 | inMinComponentArea | int | <0, INF> | 1 | Minimal area of a resulting component. Default value: 1. |
 | inRemoveBoundaryBlobs | bool | False | Flag indicating whether the blobs on border of the input region should be removed or not. Default value: False. | |
 | outComponents | System.Collections.Generic.IList<FilNet.Region> |
Description
The filter splits the input region into blobs and iteratively joins some of them into bigger components.
Only blobs that are distant from each other by at most inMaxDistance can be joined. The joining order
is determined based on modified distance between two blobs, so the closest ones are joined first.
This modified distance between two blobs is computed as follows:
- The shortest segment connecting two blobs is computed.
- The segment is scaled by \[ 0.5 \cdot (1 + inDistanceBalance) \] along the X axis and by \[ 0.5 \cdot (1 - inDistanceBalance) \] along the Y axis.
- Finally the length of the so scaled segment is computed.
Examples
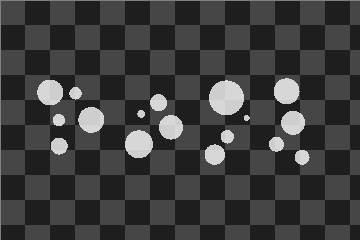 |
 |
SplitRegionIntoComponents used with inMaxDistance = 50.
Remarks
This filter is mostly used in Blob Analysis Technique please refer to our Machine Vision Guide - Blob Analysis article.
Hardware Acceleration
This operation supports automatic parallelization for multicore and multiprocessor systems.
Hardware acceleration settings may be manipulated with Settings class.

