You are here: Start » Program Examples » Globe Flattening
Globe Flattening
Aim
The aim of the program is to extract a spherical surface and transform it into a flat rectangle.
Input
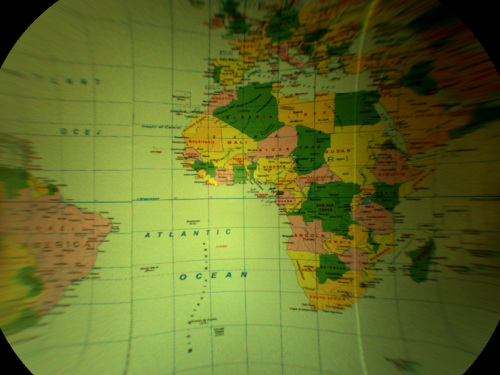
The image of a globe.

Output
A flattened image of the globe.
Hints
An image presenting a globe can be flattened in several ways, but the easiest one is to think of the globe as a sphere and consider one of the Image Spatial Transforms Maps filters to create a proper map and then display it as an image.
Labeling connections is explained in this article.
Solution (FIS)
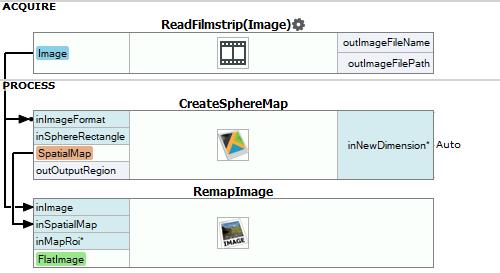
- Add LoadImage filter.
- Add CreateSphereMap filter.
- Connect outImage from previous filter with inImageFormat of the current one.
- Click on the inSphereRectangle filter and then specify the area to be flattened by clicking inSphereRectangle in Properties window:
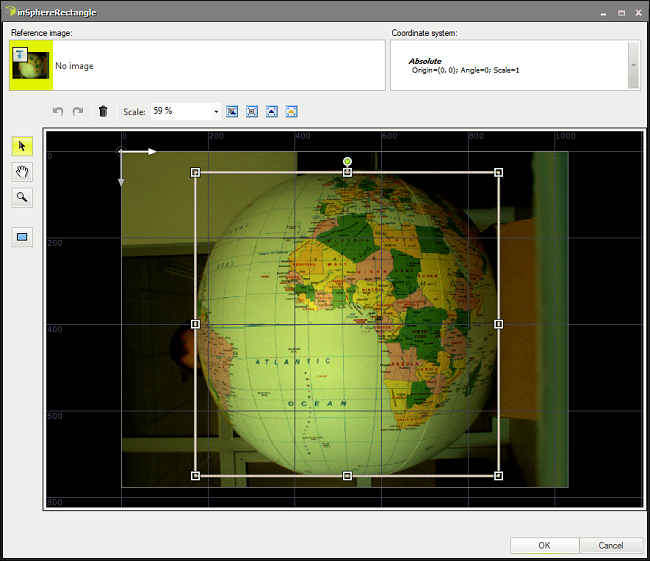
- Set inSphereRadiusCorrection to 60. It determines how many pixels the sphere radius is larger than the visible circle radius.
- Set inMargin to 260 to display only remapped area without unnecessary margin. Margin is the width of the sphere extreme points zone excluded from spatial map.
- Add RemapImage filter.
- Connect outImage from LoadImage filter with inImage of the current one.
- Connect outSpatialMap from the previous filter with inSpatialMap of the current one.
Macrofilter Main
Used Filters
| Icon | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CreateSphereMap | Inspection of the surface of balls and other spherical objects. The result is used by RemapImage. | |
| RemapImage | Fast (precomputed) image transformations, especially for view undistortion or object geometry correction (e.g. pos recognition of labels on cylindrical bottles). |
Further Readings
- Image Processing - A comprehensive introduction to Image Processing.

