You are here: Start » FIL.NET » Function Reference » Region » Region Morphology » FIL.ErodeRegion
Performs a morphological erosion on a region using a predefined kernel.
| Namespace: | FilNet |
|---|---|
| Assembly: | FIL.NET.dll |
Syntax
public static void ErodeRegion ( FilNet.Region inRegion, FilNet.KernelShape inKernel, int inRadiusX, int? inRadiusY, FilNet.Region outRegion )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Range | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | inRegion | FilNet.Region | Input region. | ||
 | inKernel | FilNet.KernelShape | Kernel shape (predefined). | ||
 | inRadiusX | int | <0, INF> | 1 | Nearly half of the kernel's width (2*R+1). Default value: 1. |
 | inRadiusY | int? | <0, INF> | Nearly half of the kernel's height (2*R+1), or same as inRadiusX. Default value: ftl::NIL. | |
 | outRegion | FilNet.Region | Output region. |
Description
The operation performs a morphological erosion, which is a basic tool used for region shrinking. Similarly to other region morphology operations, erosion is conducted using a shape called kernel (or structuring element). The kernel is repeatedly centered at each location within the dimensions of the input region. Then, pixel location L is added to the resulting region if and only if all of the input region pixels lies inside the kernel centered at this (L) location.
The input parameter inKernel allows to choose the shape of a kernel, while parameters inRadiusX, inRadiusY allow to determine its dimensions. For instance:
- inKernel = Ellipse together with inRadiusX = inRadiusY results in shrinking performed equally in all directions.
- Setting inRadiusX to higher value than inRadiusY results in shrinking performed more significantly along horizontal axis.
Examples
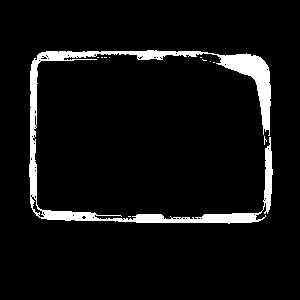 |
 |
ErodeRegion run with inKernel = Ellipse of dimensions inRadiusX = 3, inRadiusY = 3.
Errors
List of possible exceptions:
| Error type | Description |
|---|---|
| DomainError | Unsupported kernel in ErodeRegion. |

