Back to FabImage Library website

You are here: Start » Function Reference » Computer Vision » 2D Edge Detection » DetectRidges_AsRegion
DetectRidges_AsRegion
| Header: | FIL.h |
|---|---|
| Namespace: | fil |
| Module: | FoundationBasic |
Extracts a pixel-precise region of bright or dark thin lines.
Applications: Consistent detection of thin structures like scratches, cracks or lines.
Syntax
C++
C#
void fil::DetectRidges_AsRegion ( const fil::Image& inImage, ftl::Optional<const fil::Region&> inRoi, float inStdDevX, ftl::Optional<float> inStdDevY, float inRidgeThreshold, float inRidgeHysteresis, fil::Polarity::Type inPolarity, const int inMinBlobArea, fil::Region& outRidgeRegion )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Range | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inImage | const Image& | Input image | ||
 |
inRoi | Optional<const Region&> | NIL | Region of interest | |
 |
inStdDevX | float | 0.0 - 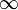 |
3.0f | Smoothing standard deviation (horizontal) |
 |
inStdDevY | Optional<float> | 0.0 - 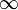 |
NIL | Smoothing standard deviation (vertical, or Auto = horizontal) |
 |
inRidgeThreshold | float | 0.0 - 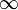 |
5.0f | Sufficient ridge strength; ridges of that strength will always be detected |
 |
inRidgeHysteresis | float | 0.0 - 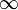 |
4.0f | Value by which the ridge threshold is decreased for ridge points neighboring with sufficiently strong edges |
 |
inPolarity | Polarity::Type | |||
 |
inMinBlobArea | const int | 0 -  |
1 | Minimal area of a ridge blob |
 |
outRidgeRegion | Region& |
Hints
- Connect an input image to the inImage input.
- Set inPolarity in accordance to which type of thin lines you want to detect.
- Start with inRidgeHysteresis = 0 and set inRidgeThreshold so that each important edge is at least partially detected. Then keep increasing inRidgeHysteresis until the edges are detected completely.
- If the edges are rugged or there are too many false edges, then try increasing inStdDevX.
Hardware Acceleration
This operation supports automatic parallelization for multicore and multiprocessor systems.

