You are here: Start » Function Reference » Barcodes » ReadMultipleBarcodes
ReadMultipleBarcodes
| Header: | FIL.h |
|---|---|
| Namespace: | fil |
Detects and recognizes multiple barcodes on the input image.
Syntax
void fil::ReadMultipleBarcodes ( const fil::Image& inImage, ftl::Optional<const fil::Rectangle2D&> inRoi, ftl::Optional<const fil::CoordinateSystem2D&> inRoiAlignment, ftl::Optional<fil::BarcodeFormat::Type> inBarcodeFormat, float inMinGradientLength, int inBaseBarWidth, int inDetectionScanCount, const int inReadingScanCount, const int inScanWidth, const float inMinStrength, const float inSmoothingStdDev, ftl::Array<fil::Rectangle2D>& outBarcodePositions, ftl::Array<ftl::String>& outDecodedTexts, ftl::Optional<ftl::Array<fil::BarcodeFormat::Type>&> outBarcodeFormats = ftl::NIL, ftl::Optional<fil::Rectangle2D&> outAlignedRoi = ftl::NIL, ftl::Optional<ftl::Array<fil::Rectangle2D>&> outBarcodeCandidates = ftl::NIL, fil::Image& diagGradientImage, ftl::Array<ftl::Array<fil::Segment2D> >& diagScheduledScanSegments )
Parameters
| Name | Type | Range | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
inImage | const Image& | Input image | ||
 |
inRoi | Optional<const Rectangle2D&> | NIL | Range of pixels to be processed | |
 |
inRoiAlignment | Optional<const CoordinateSystem2D&> | NIL | Adjusts the barcode rectangle to the position of the inspected object | |
 |
inBarcodeFormat | Optional<BarcodeFormat::Type> | EAN13 | Format of the barcode | |
 |
inMinGradientLength | float | 0.0 - 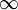 |
8.0f | Minimal gradient length of edge pixels used for detecting barcodes |
 |
inBaseBarWidth | int | 1 - 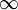 |
3 | Estimated width of the thinnest bar |
 |
inDetectionScanCount | int | 1 - 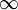 |
5 | Number of scan lines used in detecting barcode |
 |
inReadingScanCount | const int | 1 - 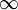 |
5 | Number of parallel scans run until first successful read |
 |
inScanWidth | const int | 1 - 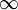 |
5 | Width of the single scan |
 |
inMinStrength | const float | 0.0 - 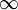 |
5.0f | Minimal strength of an extracted edge |
 |
inSmoothingStdDev | const float | 0.0 - 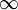 |
0.25f | Standard deviation of the gaussian smoothing applied to the profile extracted in each scan |
 |
outBarcodePositions | Array<Rectangle2D>& | Positions of the found barcodes | ||
 |
outDecodedTexts | Array<String>& | Decoded barcode content | ||
 |
outBarcodeFormats | Optional<Array<BarcodeFormat::Type>&> | NIL | Decoded barcode format | |
 |
outAlignedRoi | Optional<Rectangle2D&> | NIL | Input ROI after transformation (in the image coordinates) | |
 |
outBarcodeCandidates | Optional<Array<Rectangle2D>&> | NIL | Places with high gradient values that are further investigated | |
 |
diagGradientImage | Image& | Image of gradient directions | ||
 |
diagScheduledScanSegments | Array<Array<Segment2D> >& | Scheduled scan segments |
Optional Outputs
The computation of following outputs can be switched off by passing value ftl::NIL to these parameters: outBarcodeFormats, outAlignedRoi, outBarcodeCandidates.
Read more about Optional Outputs.
Description
Hints
- Connect inImage with the output of your image acquisition filter.
- Select inBarcodeFormat according to the type of codes you want to read. If you choose the wrong format, the codes will not be recognized. Setting its value to Auto can increase the computation time considerably. Furthermore, the Auto value causes detection of UPC-A codes as EAN-13 codes.
- If the image quality is low, increase inMinGradientLength or increase inSmoothingStdDev. The diagGradientImage output shows how this affects an intermediate image.
- If the image resolution is high, increase inBaseBarWidth or resize/downsample the input image.
Examples

Rotated barcode. |

Low quality barcode printed on plastic foil. |

Barcode on package wrapped in plastic foil. |

Barcode on blurry image. |

Barcode on standard 330ml can. |

Barcode on reflective and wrapped surface. |

EAN-13 with add-on 2 used to indicate a book edition. |

EAN-13 with add-on 5 to give a suggestion for the price. |
Remarks
Minimal bar width requirement
To provide precise detection of the barcode width of the thinnest bar should be at least 1.5 pixels.
Depending on the barcode format guard or start/end code patterns must be readable.
Pharmacode usage
The pharmacode barcode type can be read correctly in both directions. To get results from both directions use a Pharmacode and PharmacodeInversed barcode types.
Before decoding a Pharmacode the code orientation angle is normalized to a range from -45° to 135° what makes the code decoding more stable

Results of reading using a different Pharmacode directions: Pharmacode = 23 and PharmacodeInversed = 16.
Using a relative coordinate systems
Read more about Local Coordinate Systems in Machine Vision Guide: Local Coordinate Systems.
Hardware Acceleration
This operation supports automatic parallelization for multicore and multiprocessor systems.
See Also
- DetectSingleBarcode – Determines the position of a single barcode on the input image.
- DetectMultipleBarcodes – Determines the positions of multiple barcodes on the input image.
- DecodeBarcode – Translates an array of bar widths to sequence of digits or text in accordance to the selected barcode standard.
- RecognizeBarcode – Extracts information from a barcode located on the input image at a given position.

