You are here: Start » Program Examples » Radiator Holes
Radiator Holes
Aim
The task is to detect holes on the radiator and measure the distance between their centers.
Input
An image of the radiator. The position is stable, but may slightly vary.
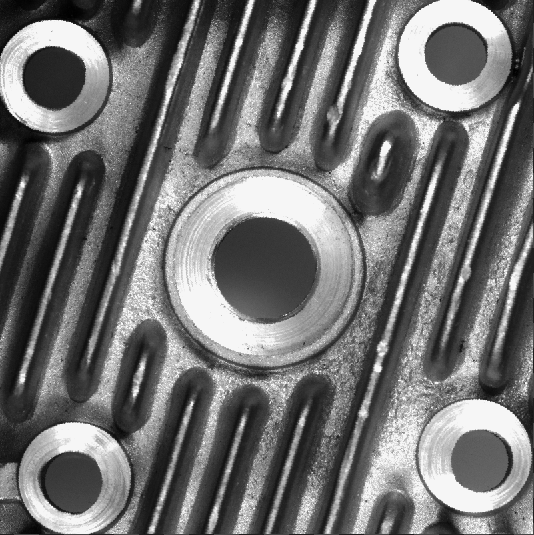
Output
Detected circles and segments between them.
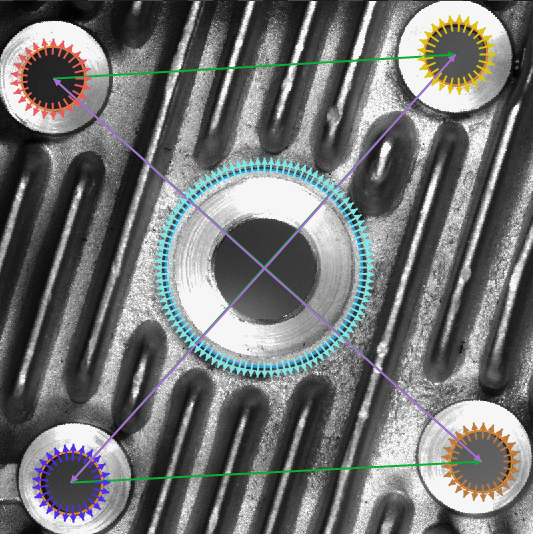
Hints
Shape Fitting allows for precise detection of line segments, circles, arcs and paths with sub-pixel precision. Therefore this technique is the best choice in cases that require high precision of the measurements, like this one. Use the FitCircle filter and remember that the right clicking on the input or the output of a filter will show advanced properties.
Solution (FIS)
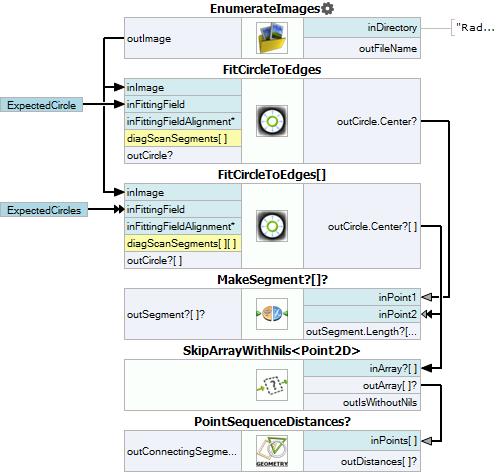
- Add filter EnumerateImages to the program and iterate it once.
- Create two Global Parameters. The first one to detect the middle circle should be of type CircleFittingField and the second one should be of type CircleFittingFieldArray. Set appropriate masks in them as shown:
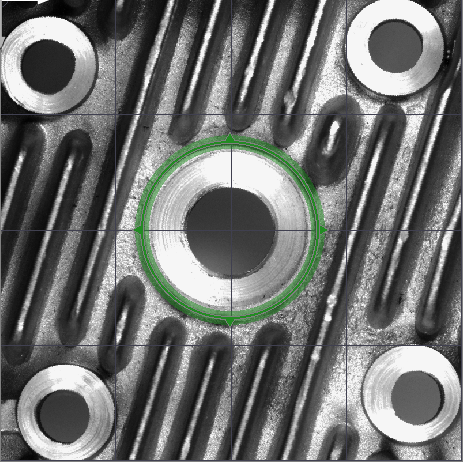
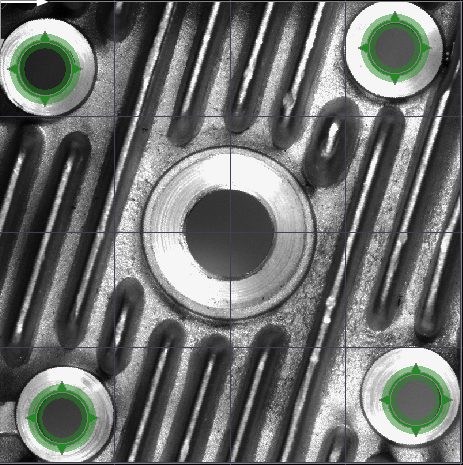
- Add two FitCircleToEdges filters and connect GlobalParameter to the inFittingField. If it is not visible, use Show/HidePorts as on the picture below:
- Set inScanCount to 100 to increase the number of points that will be searched.
-
Set inScanWidth to make a scanning field wider, so that the scanning results will be more immune to noises.
-
To create segments visible on the input image use MakeSegment filter. Connect outCircle.Center from both FitCircleToEdges filters to separate inPoint inputs. Drop outSegment on the preview window. To extract information about the length use Show/HidePorts and choose option outSegment.Length.
- Use SkipArrayWithNils to skip any data containing the Nil value. Connect outCircle.Center output where the GlobalParameter assigned to four circles is to the inArray input.
- Add the PointSequenceDistances filter that measures the distances between consecutive points in the input array. It is performed only if all the holes were detected earlier.
Macrofilter Main
Used Filters
| Icon | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FitCircleToEdges | Precise detection of a circular object or hole, whose rough location is known beforehand. | |
| SkipArrayWithNils | Changes an array with conditional elements into a conditional array. Can be useful if some processing should be performed only when all expected objects are correctly detected. | |
| MakeSegment | Creates a segment structure from individual fields. | |
| EnumerateImages | Emulates image acquisition with images stored on disk. | |
| PointSequenceDistances | Measures the distances between consecutive points of a point sequence. |
Further Readings
- Shape Fitting - This article presents usage of the Shape Fitting technique.

